Uterine Cancer
Endometrial carcinoma is one of the most common gynaecological malignancies in developed countries. Uterus is also known as the womb. Cancers that arise from the uterus are Uterine cancers. These cancers can arise from the inner or the outer lining of the uterus or the wall of the uterus. The most common site of origin is the inner lining of the uterus and cancers that arise from it are called endometrial carcinoma.
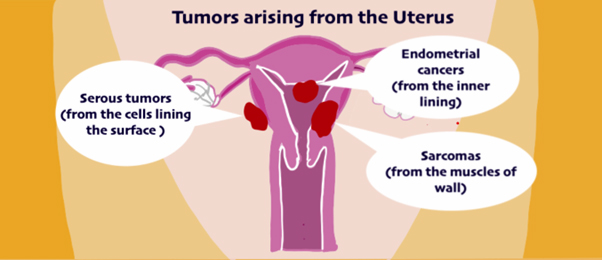
Different types of Uterine cancers :
There are 3 main types of endometrial cancer: carcinomas, sarcomas and carcinosarcomas. Carcinomas also have different subtypes and are the most common type.
Tumors that arise from the wall of the uterus are called sarcomas and those that arise from the outer lining or surface are papillary serous carcinomas that are similar to ovarian cancer.
Risk Factors :
- women who are postmenopausal, or reaching menopause late (after age 55)
- a thickened wall lining (endometrial hyperplasia)
- women who have never been pregnant
- starting periods early (before age 12 years)
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- being overweight or obese.
- family history of ovarian, uterine, or bowel cancer
- having a genetic condition such as Cowden syndrome or Lynch syndrome
- Using oestrogen only hormone replacement therapy or fertility treatment
- previous radiation therapy to the pelvis
- taking tamoxifen to treat breast cancer.
Common symptoms of endometrial cancer :
- Post menopausal bleeding (Vaginal bleeding or spotting after menopause, even a slight amount ) often leads to early diagnosis.
- Lower abdominal pain or cramping in your pelvis, just below your belly.
Diagnosis :
Blood tests:
- CA-125 assay.
Imaging tests:
- CT scans take a series of detailed pictures of the inside of your body.
- MRI scans : to see involvement of myometrium.
- Transvaginal ultrasound
Other tests:
- Endometrial biopsy inserts a thin, flexible tube through your cervix (opening of your uterus) and into your uterus to take a biopsy.
- Hysteroscopy inserts a hysteroscope, a long thin tube, through your vagina and cervix to reach your uterus. This narrow instrument with a light and camera provides detailed images of your uterus.
- Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a more complex procedure to remove uterine tissue. It takes place in the operating room.
Treatment :
In the early stages, the treatment is Surgery (removal of the uterus and lymph glands) followed by radiation therapy and chemotherapy (based on the final histopathology report). Surgery can be done with minimally invasive approach (Robotic / Laproscopy) or open surgery. At times there is a recurrence in the peritoneum or there is peritoneal spread at the time of diagnosis. Some of these patients are candidates for cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC. Endometrial cancer is an uncommon source of peritoneal cancer where as the tumors arising from the wall or the sarcomas and the serous carcinomas have a greater chance of spreading to the peritoneum.
The outcomes with Cytoreductive Surgery and HIPEC depend on the type of uterine cancer, its extent and other patient related factors. When complete removal of the tumor is possible, the outcome is most favourable.
How to reduce your risk ?
- Reduce risk by maintaining a healthy weight.
- Obesity is a major risk factor for developing endometrial cancer. The relationship between obesity and cancer is stronger for endometrial cancer than for any other type of cancer. Over 50% of endometrial cancers are attributable to obesity.
- Early detection is important for uterine cancer. If you notice any persisting symptoms, you should visit your Doctor as soon as possible. Abnormal uterine bleeding is a frequent symptom in its early stages.
