- Primary Liver cancer, which starts in the liver. Ex: HCC, Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- Secondaries in liver, here the cancer spreads to liver from other organs. Ex colon cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer
Liver Cancer
Liver cancer can be primary or secondary. Cancers which begin in the liver are called primary liver cancer. Cancers which arise in the other parts of the body and spread to liver are called secondary liver cancer or metastasis. Primary liver cancer includes
- Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (primarily bile duct cancer)
Primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) tends to occur in livers damaged by birth defects, alcohol abuse, or chronic infection with diseases such as hepatitis B and Hepatitis C, hemochromatosis (a hereditary disease associated with too much iron in the liver), non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis.
The male:female ratio for HCC in India is 4:1. The age of presentation varies from 40 to 70 years.
Secondary or metastasis in liver is the most common cancerous condition of liver. It depends on the location of the original cancer. Primary cancers that are most likely to spread to the liver are cancers of the:
- Colon
- Rectum
- Oesophagus and Stomach
- Pancreas
Even if the primary cancer is removed, liver metastasis can still occur years later. If you’ve had cancer, it’s important to learn the signs of liver metastasis and get regular checkups.
Risk Factors :
- Chronic viral infections including Hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) are the main cause of liver cancer.
- Alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis
- Aflatoxin exposure can lead to the development of Hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or genetic disorders such as haemochromatosis, or alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency.
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Tobacco smoking
- Exposure to certain chemicals
- High alcohol consumption
Signs and Symptoms :
- Jaundice - yellowish discolouration of skin and eyes
- Abdominal pain - often on the right upper abdomen
- Loss of weight and appetite
- Hepatomegaly - enlarged liver, the abdomen may appear swollen
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomitting
- Back pain
- General itching
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination: Your doctor will examine your abdomen to look for any in the upper abdomen. He also examine your eyes and skin to look for the evidence of jaundice
- Blood tests: complete blood count, LFT, RFT, Serum electrolytes, coagulation profile, HIV, HCV &HBV testing
- Tumour Markers : AFP, CEA and CA 19 9
- Radiological imaging: USG Abdomen, Triple phase CT Scan of the abdomen, MRI Abdomen, CT Angiography
- Biopsy: Liver biopsy offers a safe and effective means to confirm suspicious lesions for HCC. Cytologic and histologic samples can be obtained by percutaneous fine-needle aspiration (FNA) and needle core biopsy, respectively, under US or CT guidance. Biopsy may not be always required if Imaging features are very much suspicious of Liver cancer along with raised tumour markers.
Treatment options for Primary Liver Cancers (HCC) :
There are various modalities of treatment for HCC.
Treatment options include :
- Surgical resection of diseased liver, Liver transplantation
- Liver directed therapies like TACE, TARE.
- Ablation : MWA, RFA.
- Systemic therapy : Chemotherapy, TKi
Treatment options depend on the stage of the disease, general condition of the patient and associated comorbidities
Surgery is the best curative option amongst all modalities of treatment provided liver function and FLR is good.In patients where liver function is compromised, liver transplant may be an option in selected group of patients. They can be
- Parenchyma preserving liver surgeries.
- Parenchyma preserving liver surgeries in combination with Ablation ( For colorectal liver metastasia).
- Major Hepatectomy
Liver directed therapy (TACE, TARE) : is offered wen patients are not candidate for surgical resection. It is performed by Interventional Radiologists.
Loco regional ablative techniques are considered in patients who are not candidates for surgery ( patients with portal hypertension, poor liver functions, poor functional liver remnant (FLR) , Poor general condition, metastasis).There outcomes are as good as resection in tumours which are less than 2 cms. Ablation of liver lesions is performed along with Interventional Radiologists.
In advanced, metastatic and unresectable disease where they are not eligible for any other form of treatmet, patients will be referred to medical oncologist for chemotherapy / Immunotherapy.
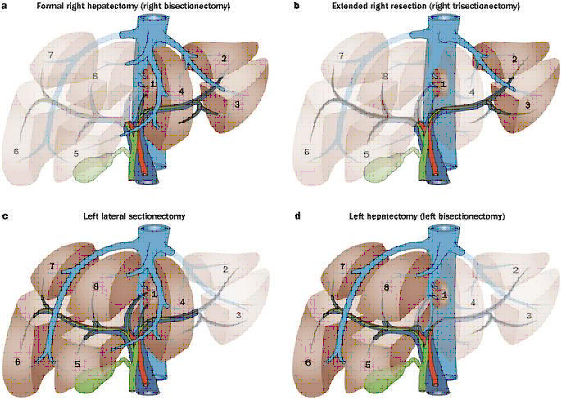
Different types of liver resection performed is based on the location and extent of tumour
Prevention
- Reduce drinking alcohol
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Get hepatitis B vaccination
- Take precautions to prevent Hepatitis C infection
-
What is liver cancer?There are two types of liver cancerSecondaries in liver are the most common cancer of the liver
-
Is cirrhosis of the liver the same thing as liver cancer ?Cirrhosis is due to do long term injury to the liver.It can be alocoholic cirrhosis or non alcoholic which can be seen in patients with fatty liver. Most common causes are hepatitis and alcohol abuse. Cirrhosis by itself is not a cancer, but increases the risk of liver cancer.
-
Can liver cancer be prevented?Once cirrhosis (or scarring of the liver) has set in, it is generally not reversible. Therefore, the best way to prevent liver cancer is to avoid liver damage by treating any underlying hepatitis and avoiding excess alcohol use.
-
What is the survival rate after the surgery for HCC?In general survival rates are higher for people who can have surgery to remove their cancer, regardless of the stage. Overall survival of over 50-70% has been seen in patients with small resectable tumours who do not have cirrhosis or other health issues. For early stage HCC with cirrhosis who have liver transplant , 5 year survival rate is 60-70%.
-
What will be the follow up duration after the treatment?You have to consult your doctor maybe every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 to 12 months. Then, the longer you’re cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. After 5 years, they may be done once a year.
-
What are the side effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy?Side effects of chemotherapy includes nausea, vomitting, hair loss, infection and loss of appetite. These symptoms will settle down once the patient has completed chemotherapySide effects of radiotherapy include, Skin changes where the radiation is given and fatigue
-
What is the survival rate in colorectal metastasis after surgery?In a solitary and resectable liver metastasis the survival rate is 60-70%, in a multiple resectable liver metastasis the survival rate is 25-30%
