Ovarian Cancer
It is most common cause of peritoneal cancer. It is the fourth most common female cancer and the 8th most common cancer in women.
The ovaries are a pair of small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus in the female reproductive system. Their primary function is to produce eggs (ova) and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. Ovaries are essential for reproductive health and play a crucial role in menstrual cycles and fertility.
What is Ovarian Cancer ?
Ovarian Cancer is a cancer that arises from the ovaries that are part of the female reproductive system. Ovarian cancer originates from the surface lining (cells on the surface) of the ovaries. In rare cases, it starts from the peritoneum which is the membrane lining the contents of the abdomen and pelvis. It can affect one or both ovaries and may spread to nearby organs and tissues if left untreated
Its Peculiarity :
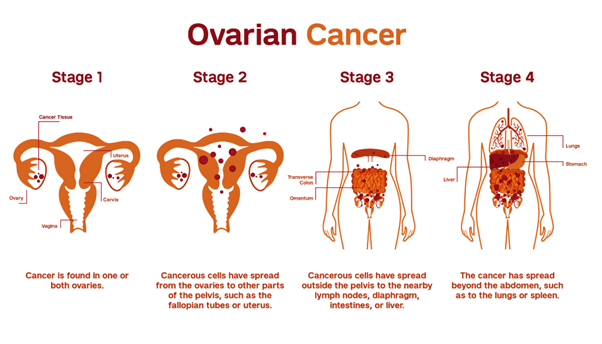
It is the most common cancer to spread to the peritoneum. It behaves very similar to primary peritoneal cancers. In all other cancers (except primary peritoneal cancers), peritoneal cancer is stage IV disease, however, in ovarian cancer, peritoneal cancer spread is seen in the second and third stages (Stages II and III). The chances of spreading to other organs like the liver, lungs and bones are lower in ovarian cancer.
The other peculiarity is that 80% of the ovarian cancers are diagnosed at a late stage. Many times, it remains asymptomatic with no signs and symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms such as abdominal bloating, pelvic pain, changes in bowel habits, and frequent urination may develop. In some women it is picked up early when scans are performed for other non-specific complaints like abdominal pain or urinary problems. The spread of cancer to the peritoneum is also very rapid in these patients and often develops only within a few months.
Risk Factors :
- Genetic mutations, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes
- Family history of ovarian or breast cancer
- Age, with risk increasing with advancing age
- Personal history of breast, uterine, or colorectal cancer
- Endometriosis, a condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus
- Hormone replacement therapy after menopause
- Obesity and lifestyle factors such as smoking and diet
- Prolonged use of fertility drugs
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer ?
Ovarian cancer rarely has noticeable symptoms when it is in its earliest stages. As the cancer progresses, subtle signs begin to appear, but you might not notice them right away, or they may be blamed on other common conditions.
The symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
- abdominal bloating or swelling
- pain in the abdomen or pelvis
- difficulty eating, or feeling full quickly
- lack of appetite
- Urinary symptoms like urgency or increase in frequency.
- change in bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea)
- back pain
- loss or gain in weight
Diagnosis :
- Pelvic exam
- Imaging tests: Tests, such as ultrasound / CT scans of abdomen and pelvis may help determine the ovarian tumor. PET scan will help to assess the spread to other parts.
- Blood tests : Routine blood tests , CA 125 and CEA levels.
Treatment :
The standard treatment for ovarian cancer is a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Chemotherapy can be either before surgery or after surgery which is decided based on the extent of the disease. Surgery includes removal of the uterus and ovaries, the omentum and other regions bearing tumour which is called as Cytoreductive surgery.
Whether chemotherapy is administered first or whether the surgery is performed first, radical surgery is essential to prolong the survival and delay recurrence.
Surgical Approaches :
The goal of surgery is to remove as many cancerous cells as possible. Depending on the type , stage and extent of the disease, surgical options may include :
- Fertility sparing surgery
- Debulking / Cytoreductive surgery.
Fertility sparing surgery may be unilateral or bilateral oophorectomy (removal of one or both ovaries). Radical surgery includes removal of both ovaries , hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), lymphadenectomy ( extent depends upon intra operative findings ) and omentectomy (removal of the fatty tissue covering the abdominal organs).
Conventional surgery that is performed for ovarian cancer is referred to as debulking surgery. The uterus and ovaries are removed along with the omentum and regional nodes. Peritoneal disease is usually not addressed or only small areas of the peritoneum are removed.
In Cytoreductive surgery, the entire region of the peritoneum that has tumor deposits is removed.It may also involve removal of other nearby structures if they are involved by the disease. In addition, some areas that have a higher chance of bearing microscopic disease are removed like the greater and lesser omentum. This is a more effective way to treat the disease. In addition to the disease or tumor deposits that are visible to the surgery, there is a very high chance of microscopic or invisible disease in the surrounding peritoneum that seems to be normal. In cytoreductive surgery, this peritoneum is removed which reduces the probability of the tumor coming back. It has shown to have better long term survival outcomes
Advanced treatment options :
HIPEC :
HIPEC adds to the benefit of radical surgeries. It helps in treating the microscopic disease more effectively leading to reduced risk of recurrence and delays the recurrence as well. Some studies have also shown that the incidence of peritoneal recurrence is reduced with HIPEC.
The most common chemotherapy drug used for HIPEC is Cisplatin and Doxorubicin. In ovarian cancer, cisplatin resistance is a major problem leading to early recurrence and shorter survival. Heat used in HIPEC can be useful in overcoming Cisplatin resistance.
Very old and frail patients may not be able to tolerate HIPEC. Similarly those who have kidney dysfunction, uncontrolled diabetes or other major health issues are not subjected to HIPEC to avoid severe complications.
Currently, HIPEC is recommended to only select a group of patients with ovarian cancer. It is only performed for patients with ovarian cancer undergoing surgery after a few cycles of chemotherapy. In this scenario, performing HIPEC in addition to cytoreductive surgery has shown better survival outcomes.
PIPAC :
PIPAC is given to patients who have received chemotherapy earlier and usually more than one type of chemotherapy.
This method is actually used to control the symptoms and reduce the disease burden in the cancer patient, for further treatment.
In some cases the tumor can disappear completely or may reduce drastically post PIPAC and the surgical removal of the remaining tumor can be performed effectively. These patients may experience a prolonged survival post treatment.
PIPAC is used primarily for patients in whom the disease is extensive and cytoreductive surgery with or without HIPEC is not possible. It is not an alternative for cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC
Patients who are bed ridden and cannot eat, have symptoms of intestinal obstruction,, those who are malnourished , do not benefit from PIPAC. Sometimes there are adhesions between the intestines and abdominal wall due to which laparoscopy is not possible and hence these patients cannot receive PIPAC.
Which therapy is better - HIPEC or PIPAC ?
HIPEC is a single treatment usually given during open surgery and higher doses of chemotherapy drugs are used in it. PIPAC is given laparoscopically and multiple sessions are possible, doses of drugs used are lower.
At present, both have different uses. HIPEC is used along with radical surgery that comprises of complete tumor removal (cytoreductive surgery). It can cure certain patients.
PIPAC is used for patients who cannot undergo HIPEC. Its role is palliative. Some times PIPAC is used to shrink the tumor before cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC.
Cytoeductive surgery and HIPEC require a greater expertise to perform compared to PIPAC.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancerous cells. To limit side effects and damage to healthy cells, ovarian cancer patients are usually given chemotherapy in cycles with several rest periods. Chemotherapy may be recommended before or after surgery, or both.
In some patients, when the disease is very extensive, chemotherapy is given first and surgery is performed after 3-4 cycles of chemotherapy. The remaining cycles of chemotherapy are given after surgery. Some patients with extensive disease may require maintenance therapy for 1-2 years.
Fertility Preservation
We offer ovarian cancer patients options to preserve fertility for :
- For patients with early stage ovarian cancer ( also depending on the histologic type and spread ) , it may be possible to surgically treat ovarian cancer by removing only one ovary and fallopian tube.
- Techniques :
- Egg and embryo freezing.
- Preservation of ovarian tissue. /li>
Ovarian Cancer Prevention and Screening
Prevention Strategies :
Women can reduce their risk for ovarian cancer by achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and not taking hormone therapy after menopause. Women with a family history of cancer may want to discuss oral contraceptives and genetic testing.
Ovarian Cancer Screening
There is currently no effective screen for ovarian cancer. Prompt recognition and evaluation of suspicious symptoms is essential to avoid delays in diagnosing the disease.
-
Are Fibriods or Ovarian cysts related to cancer ?Fibroids are not related to ovarian cancer, and most ovarian cysts are not cancerous (and will not develop into cancer). However, some complex ovarian cysts may be cancerous and should be monitored by your doctor.
-
Can I have children after ovarian cancer diagnosis ?If you are diagnosed with ovarian cancer and if you are ideal candidate for fertility preservation , then we will evaluate your options for having a family in the future. This might include egg preservation, in-vitro fertilization and other advanced reproductive techniques.
