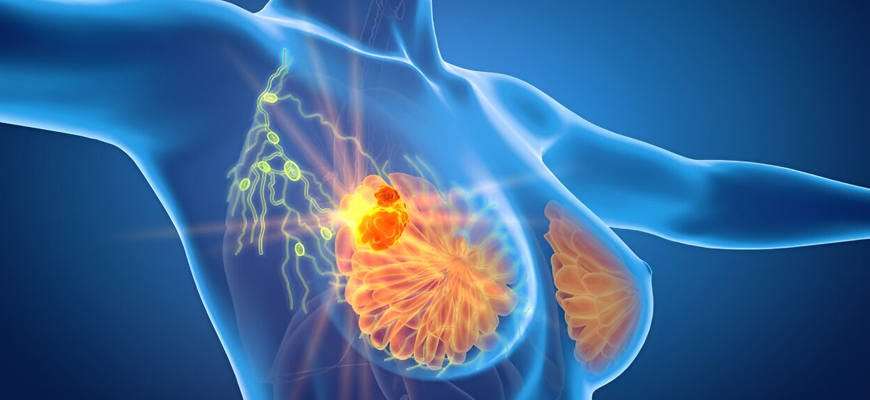
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the one of the most common forms of cancer, and the second most common cause of cancer-related death among women globally
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
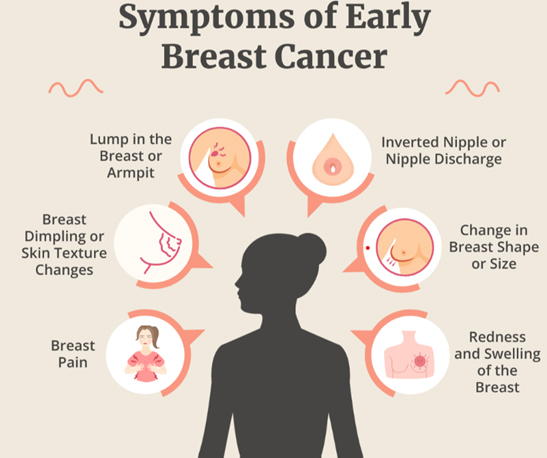
Breast cancer signs and symptoms can be different in every patient. But most will have a painless lump, slight pain or lump in their breast, which has been present over a period of time. Very rarely these lumps can be associated with pain.
Breast cancer may not cause any symptoms in its early stages. A tumour may be too small to feel in many cases, yet an abnormality on a mammogram can be observed.
Common signs of breast cancer include:
- Presence of lump
- Nipple retraction
- Nipple Puckering or retraction
Risk Factors :
- Age
- Breast cancer or benign (non-cancerous) breast disease history
- Breast cancer risk is inherited, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations
- Dense breast tissue
- A reproductive history that leads to increased estrogen exposure
- Menstruating at a young age
- Being older when you first had a child or never having had a child
- Begin menopause at a younger age
- Using hormone therapy to ease the signs of menopause
- Use of radiation therapy in the breast or chest
- Obesity
Diagnosis :
Following tests and procedure are done :
- Breast Exam :
To feel for lumps or other irregularities in your breasts and the lymph nodes in your armpit. - Mammogram :
A mammogram is a kind of X-ray used to detect any non palpable tumors or palpable tumors with changes in breast parenchyma of the breast. This test can help to find out tumors at an early stage.Breast cancer screening via mammogram is done evry often. If screening mammography reveals an anomaly, your doctor may prescribe further tests . - Ultrasound of the Breasts :
- Biopsy (removal of a sample of breast cells for testing) :
Core biopsy is done under local anaesthesia on opd basix in case of palpable tumors, When a tumour is not palpable,it can be done under USG guidance. A biopsy is a procedure in which a core of tissue from a suspicious area using a biopsy gun taken . A small metal marker is often left at the spot inside your breast so that subsequent imaging tests may readily identify the region. - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast :
An MRI machine creates images of the inside of your breast using a magnet and radio waves. You will be given a dye injection before your breast MRI. An MRI does not employ radiation to produce pictures, unlike other forms of imaging procedures.
A new breast lump may be diagnosed by ultrasound to see its nature whether it’s a solid mass or a fluid-filled cyst.
A biopsy sample is also examined to establish the cells involved in breast cancer, the tumor’s grade, and whether the cancer cells contain hormone receptors or other receptors that might affect your treatment choices.
Treatment :
There are different treatment options for breast cancer depending on the extent of the disease and stage of cancer. Treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy or a combination of these.
- Surgery :
- Lumpectomy : It is a surgical procedure that involves removing the cancer while leaving as much normal breast as possible. Some surrounding healthy tissue and lymph nodes are usually also removed.It is also known as breast conservation surgery because it removes only the tumor while maintaining the healthy tissue around it without removing the breast. Breast-conserving surgery allows a woman to keep most of her breast, but makes it likely she will also need radiation. Not all women with breast cancer are candidates for BCS.
- Mastectomy : A modified radical mastectomy is a procedure in which the entire breast is removed, including the skin, areola, nipple, and most axillary lymph nodes, but the pectoralis major muscle is spared.
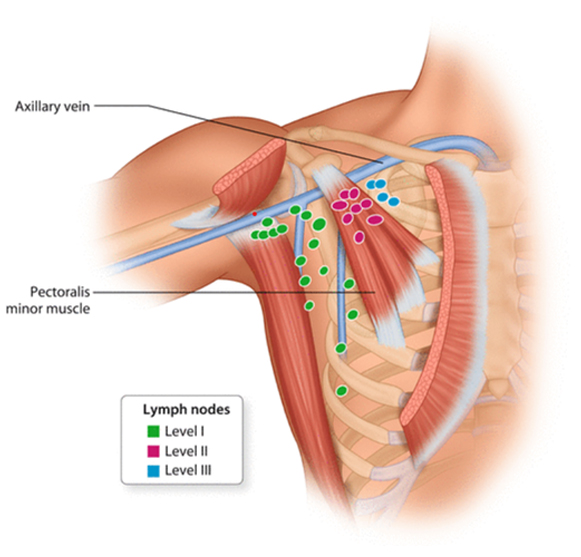
- Axillary Surgery : It is a part of Breast cancer surgery and it helps to decide decide the stage of the disease, the chances of recurrence, the need of chemotherapy, and
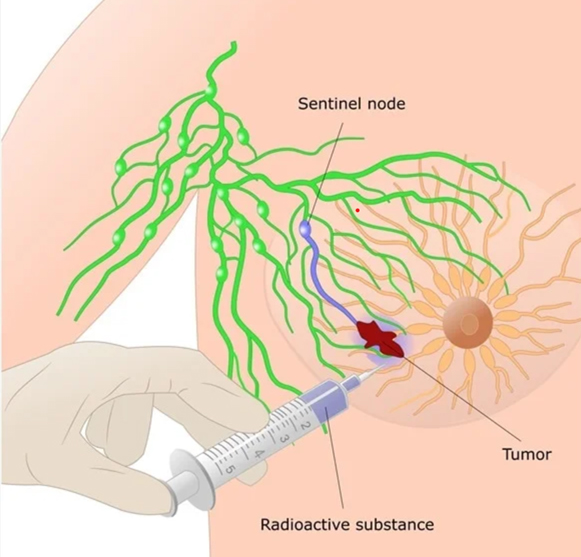
- Sentinal Lymph node biopsy : Sentinel lymph node mapping came helps to minimise the morbidity arising out of a conventional complete axillary dissection. SLNB is a technique to find out which of the lymph nodes are harbouring cancer cells. These lymph nodes are biopsied (taken out) and sent for microscopic examination.
- Axillary lymph node dissection : This is performed in patients whom lymph nodes are positive or sentinel lymph node biopsy is positive for metastasis to the nodes. Compared to sentinel node biopsy , ALND carries a higher risk of lymphoedema , chronic pain and recurrent lymphangitis in the affected arm.
- Chemotherapy : Uses anti-cancer drugs to destroy cancer. They are given either before surgery ( Neoadjuvant ) to decrease the size of tumor and make it amenable for breast conservation or after surgery in the adjuvant setting to reduce the risk of recurrence. Not all patients require chemotherapy. Those diagnosed early may not require chemotherapy.
- Radiation Therapy : It is offered to patients who have undergone Breast conservation or after surgery in the adjuvant setting ( based on final histopathology report ) to reduce the risk of local recurrence.
- Targeted therapy
- Hormonal therapy
Prevention of Breast cancer :
- Maintain a healthy weight : Patients who are overweight, especially after menopause, have an increased risk of developing breast cancer. Researchers believe this is because fat tissue can produce estrogen (and estrogen exposure is linked to breast cancer).
- Limit or avoid alcohol :Any amount of alcohol increases your risk for breast cancer. Greater alcohol consumption is linked to higher breast cancer risk.
- Stay active : We recommend:
- Getting a weekly total of 150 to 300 minutes of moderately intense activity (exercise that you can do while holding a conversation), or 75 to 150 minutes of vigorous activity, or a combination of the two
- Strength training and stretching to improve balance and flexibility about twice a week
- Limiting sedentary activities, such as watching TV
- Eat a healthy diet : We recommend a plant-based diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, fruits and beans. Incorporate brightly colored or strongly flavored vegetables and fruits into your diet. Limit red and processed meats, sugary drinks and sodas, and processed foods high in fat and starch.
- For new mothers, consider breastfeeding , Studies show that breastfeeding for at least one year is associated with a decreased risk of breast cancer. However, the decision on whether to breastfeed your baby is a personal one. The knowledge that breastfeeding may slightly reduce breast cancer risk is just one of the many factors to weigh.
- Avoid smoking : Although the association between smoking and breast cancer risk isn't clearly established, smoking is strongly discouraged because it clearly raises heart disease and lung cancer risks.
- Manage stress.
Breast cancer Screening :
- Breast self-exammination :While many women choose to perform breast self-exams, they are not specifically recommended for breast cancer screening. Breast changes can occur due to a number of reasons, including pregnancy, aging, and hormonal changes.
- Clinical breast examination : Considered one of the most sensitive ways to screen for breast cancer.
- Mammogram:The most common screening method, mammograms are X-rays of the breast that can detect tumors too small to feel. There are different types of mammograms, including film, digital, and digital breast tomosynthesis.
The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends that women who are 40 to 74 years old and are at average risk for breast cancer get a mammogram every 2 years.
